Introduction to IRDAI
To provide for the establishment of an Authority to protect the interests of holders of insurance policies, to regulate, promote and ensure orderly growth of the insurance industry and for matters connected therewith and further to amend the Insurance Act, 1938, the Life Insurance Corporation Act, 1956 and the General Insurance Business(Nationalization) Act, 1972.
Insurance Regulatory Development Authority of India: Composition and Authority:
All above person are appointed by the central government.Person having ability, integrity and having knowledge in finance accounts, general insurance, life insurance, actuarial science, economics, law, accountancy, administration, or any other discipline which would, in the opinion of the Central Government, be useful to the authority.
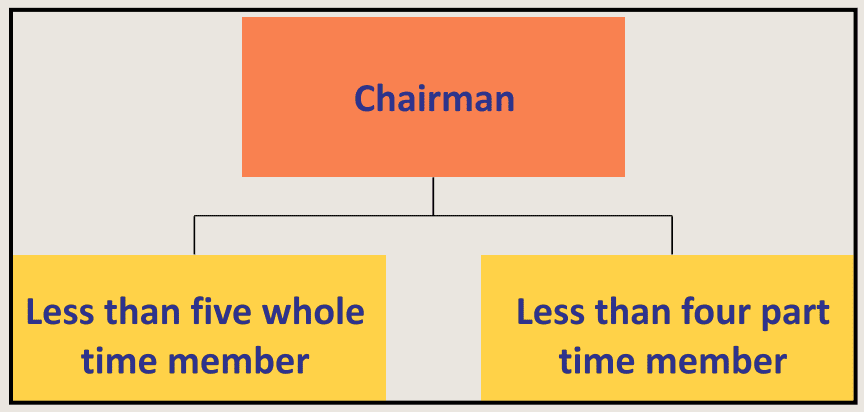
Tenure of the chairperson and member:
The chairperson and whole time member shall hold office for five year and shall reappointed.No chairman shall hold office after attainment of his age sixty five year.No member shall hold office after attainment of his age sixty two year.A part-time member shall hold office for a term not exceeding five years.
Removal from Office
Central government may remove member in the following cases: the member who,
Has at any time has been, adjudged as an insolvent; orHas become physically or mentally incapable of acting as a member; orHas been convicted of any offence which, in the opinion of the Central Government, involves moral turpitude; orHas acquired such financial or other interest as is likely to affect prejudicially his functions as a member; orHas so abused his position as to render his continuation in office detrimental to the public interest.
History of insurance in India:
In India insurance was mentioned in the writings of Manu (Manusmrithi), Yagnavalkya (Dharmasastra and Kautilya (Arthashastra), which examined the pooling of resources for redistribution after fire, floods, epidemics and famine. the lifeinsurance business began in 1818 with the establishment of the Oriental Life Insurance Company in Calcutta. the company failed in 1834. In 1829, Madras Equitable began conducting life-insurance business in the Madras Presidency. The British Insurance Act was enacted in 1870, and Bombay Mutual (1871), Oriental (1874) and Empire of India (1897) were founded in the Bombay Presidency. The era was dominated by British companies.
Facts
The Indian Life Assurance Companies Act, 1912 was the first statute regulating life insurance.In 1928 the Indian Insurance Companies Act was enacted to collect the information about life and non-life insurance business conducted by the Indian and foreign companies.On January 19, 1956, life insurance sector was nationalized and Life Insurance Corporation was established.The LIC absorbed 154 Indian and 16 non-Indian insurers and 75 provident societies.Until late 1990 LIC had monopoly before.General insurance in India began during the 17th century.In 1907 the Indian Mercantile Insurance was established, the first company to underwrite all classes of general insurance.In 1957 the General Insurance Council (a wing of the Insurance Association of India) was formed, framing a code of conduct for fairness and sound business practice.170 insurer were amalgamated and was group into National Insurance Company, New India Assurance Company, Oriental Insurance Company and United India Insurance Company.In 1972, with the passage of the General Insurance Business (Nationalization) Act,the insurance industry was nationalized on 1 January 1973.In 1993, the central government has set up a committee chaired by the RBI governor R. N. Malhotra to propose recommendation to reform finance sector. Committee has recommend to permit private sector in insurance industry. And foreign company with the joint venture of indian companies.On the recommendation of the Malhotra committee government has set up IRDAI (Insurance Regulatory and development Authority of India) in April 2000.Objectives of the IRDA include promoting competition to enhance customer satisfaction with increased consumer choice and lower premiums while ensuring the financial security of the insurance market.The IRDA opened up the market in August 2000 with an invitation for registration applications; foreign companies were allowed ownership up to 26 percent.In 2013 the IRDAI attempted to raise the foreign direct investment (FDI) limit in the insurance sector to 49 percent from its current 26 percent. The FDI limit in the insurance sector was raised to 100 percent according to the budget 2019.
If you have any query regarding Introduction to IRDAI then please let us by comment section. Recommended
Best Term Insurance Policy in IndiaDifference between Post Life Insurance and LICLife Insurance PolicyDeductions Under Section